Transforming the Manufacturing Industry: The Power of Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
In manufacturing, artificial intelligence (AI) refers to a machine’s capacity to think like a human, react autonomously to both internal and external events, and predict future events. The robots can identify problems and act to resolve them when a tool breaks down or anything unexpected—or possibly even something unexpected—happens.
Automating challenging tasks and identifying hidden patterns in workflows or production processes are two aspects of artificial intelligence used in manufacturing.
Thanks to AI and machine intelligence, manufacturers today have the unequaled ability to increase throughput, manage their supply chain, and accelerate R&D.
What Justifies the Use of AI in the Manufacturing Sector?
In the industrial industry, artificial intelligence (AI) handles jobs including welding, painting, assembling, and material handling. It accomplishes this with an accuracy on par with the greatest human workers.
Additionally, AI is capable of controlling workflows without any mistakes or delays. Machines do not require rest; you can push them to their absolute limits without worrying about how it will affect their health or performance.
Additionally, AI can assist manufacturers in tracking intricate procedures, equipment, or workflows in real-time, allowing them to spot dangers and implement data-driven preventative maintenance strategies.
AI can save time in the industrial sector because of these beneficial aspects.
What Are the Applications of AI In Manufacturing?
- Predictive maintenance: Predictive maintenance is a significant advantage of artificial intelligence for the industrial industry. By doing so, firms may better understand the condition of their machinery, cut downtime, and maximize asset use.
- Energy Efficient: A factory’s energy efficiency can be improved with the aid of artificial intelligence. Manufacturing companies may streamline and automate routine operations like supply chain management, process design, and resource management by “listening” to their equipment and making sense of massive datasets.
- Packing and Packaging: By enabling manufacturers to see, hear, and touch equipment and conveyor belts, the internet of things (IoT) is enabling them to optimize the packaging process.
- Quality Control: AI in manufacturing can be used to prioritize defects and identify patterns of them, saving businesses time and money. Additionally, it can boost yield and lower the possibility of releasing faulty goods onto the market by optimizing inspection procedures.
Work of AI and Robotics in Manufacturing Field
Here are a few of the main businesses that are utilizing machine learning-based methods to advance the manufacturing industry. They include Siemens, General Electric. The specifics of how various businesses are utilizing this new technology are as follows:
Siemens
They monitor their steel factory using a neural network. They were able to build AI for manufacturing purposes because to this. Siemens introduced Mindsphere, an intelligent cloud designed to track machine fleets for maintenance needs. Mindsphere is now in testing. Their main objective is to track, document, and examine all connected activities from design to recovery. so that they can quickly identify and fix any errors. The most significant AI-related accomplishment of Siemens is the ability to reduce emissions from a particular gas turbine better than any person. The newest gas turbines include 500 sensors that continuously measure temperature, pressure, and other variables.
A story published on the Siemens website claims that scientists have created a two-armed robot with artificial intelligence that can produce goods without the need for programming. The task is divided up among the robot’s arms independently, and it is finished faster as a team. At Siemens Corporate Technology (CT), the company’s international research division, in Munich, the function of the hands was shown. The autonomous optimization of gas turbines, as well as the monitoring and maintenance of the smart grid and other industrial units, have all been accomplished with the help of artificial intelligence. Siemens is utilizing artificial intelligence in several industries and upgrading the power grid by giving it tools for network monitoring and management.
General Electric (GE)
Their primary goal is to transform them into smart units, and they have more than 500 factories around the world. GE developed the Brilliant Production suite as a system to monitor and manage every aspect of the manufacturing process and address any problems or inefficiencies before they arise. The purpose of GE’s Brilliant Manufacturing Suite is to integrate design, engineering, manufacturing, supply chain, distribution, and services into a single, intelligent system that is scalable around the globe. Recent reports state that efforts are being made to check difficult-to-reach locations using drones, crawling robots, AI, and predictive analytics. Industrial units will be able to optimize and maintain themselves as a result. Avitas Systems was founded by GE Ventures to use robotics and artificial intelligence to advance the inspection services sector.
They are developing a cloud-based system that will access and analyze data from sensors on those drones hosted on GE’s Predix software. Unmanned drones with sensors can withstand the heat with ease. They can utilize infrared cameras and other sensors to find issues before they arise. Data will be collected by these drones and fed to the Avitas Systems platform. The system tracks changes over time and suggests inspection and maintenance based on the data.
2020 global manufacturing industry use cases
Many respondents (59 percent) believe that quality control is the most significant application of artificial intelligence in the manufacturing sector. In most cases, quality control refers to putting in place measures that standardize output. Artificial intelligence, for instance, can assist in enhancing overall quality control by utilizing smart cameras to enhance inspection procedures, which results in lower costs. The manufacturing sector includes businesses that turn raw materials and component parts into finished goods.
Exhibit 1
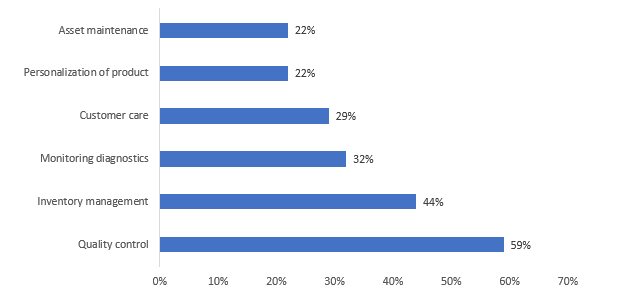
What Benefits Can Artificial Intelligence Bring to Manufacturing?
- Eliminate Bottlenecks: In the era of Industry 4.0, bottlenecks have been replaced by fresh opportunities that are simple to spot, analyze, and take advantage of.
- Eliminate Hidden Expenses: Manufacturers can uncover hidden costs in their processes that frequently go unnoticed when they are only considering the normal costs by using the power of data analytics.
- Reduce Problems: Because manufacturers can now pinpoint the source of errors, they are less likely to occur again.
- Prediction: AI has the ability to foresee a variety of situations, including chemical leaks, fires, malfunctioning machinery, and component failure.
What Are the Challenges of Using AI in The Manufacturing Sector?
Will AI cause a large number of job losses? To answer the topic, we must first define “full automation,” which is the term used to describe every process or job that has been entirely automated with robotics and AI. Manufacturers cannot anticipate this because “people plus AI” increases productivity by 30%. The 30% does not, however, allude to a specific amount. In the upcoming years, it will rise due to increased investments and research. Therefore, full automation does not pose a danger to jobs.
Will security worries increase because of AI? It is necessary to distinguish between physical security and cyberattacks while addressing this question’s security problems. Since people will be in charge of operating factory robots on a daily basis, physical security is most likely to be a concern. On the other side, most IT infrastructure is impacted by cyber-attacks. AI can lessen the likelihood of cyberattacks because it uses huge data in its operations.
It is reasonable to anticipate that manufacturing processes will change as AI becomes more and more ingrained in our daily lives.
Companies are currently treading lightly and making little adjustments rather than going all in. The development of artificial intelligence still requires a lot of work. There isn’t yet a certain winner as a result.
But makers need to understand that AI is not a “one and done” technology. It will call for more money and a dedication to digital transformation.
According to a blog post by AI software developer IPsoft, “lack of talent and an aging workforce” is another issue facing AI in manufacturing. “Many worry they’ll be left behind in this new revolution as the manufacturing industry quickly begins changing into the digital era, migrating from manual work to automation.”
Conclusion
AI may considerably assist in ensuring the viability of your manufacturing company even in the face of continual transformation. It provides predictive analytics to help manufacturers make wiser decisions. The benefits of artificial intelligence are numerous, ranging from customer management to product design. Improved process quality, a more efficient supply chain, adaptability, etc. are a few of them.
But there are a number of issues with AI technology. Costly as well as vulnerable to hacks. But these disadvantages are outweighed by AI’s advantages.
Author: Sonu Kumar Sah
