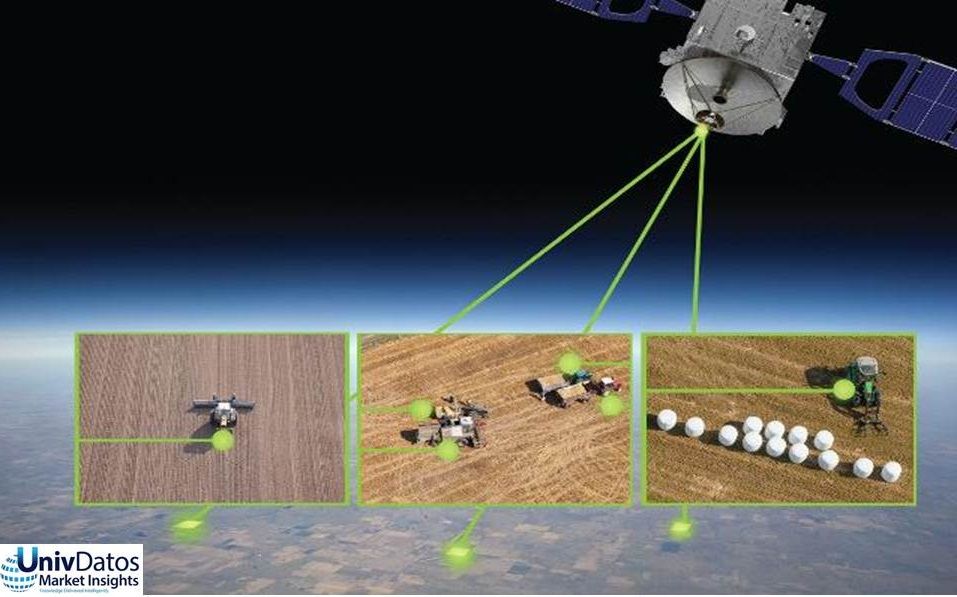
Precision Agriculture, Satellite Farming Or Site-Specific Crop Management
Precision Agriculture, Satellite Farming or Site-Specific Crop Management
Precision agriculture is based on observing, measuring and responding to inter and intra-field variability of crops to manage crop farming. Precision agriculture is also known as satellite farming or site-specific crop management process. Nowadays, in agriculture, plant breeding and genetic transformation have gained much importance as it accelerates crop quality which ultimately improves the overall productivity of the land. There are several companies which have started investing in agricultural start-ups since 2015 with an aim of transforming farming into big data industry.
To estimate plant health, companies are providing solutions such as cloud-based analytical capabilities, unmanned aerial vehicles and multispectral cameras which help in proper estimation of plant’s health. In addition, these sensors are connected to the internet with the help of a wireless communication system for the inclusion of data in the farm database and mapping systems for analysis. This enables real-time availability of data and analytical capabilities.
Analytics is disrupting agricultural industry in multiple ways:
- Accurate Crop predictions: Farmers, with the help of analytical companies, are using sophisticated computer algorithms to analyze and make accurate predictions of weather and crop data before planting seeds, which in turn allows them to harvest crops at the optimum time to maximize crop yield.
- Seed Engineering: Scientists have been analyzing plant data to envision a plan of developing crops that could grow in any climatic condition. These special seeds are designed after using big data which can put an end to the world of hunger.
- Automation in Agriculture: With the help of recent advancements in technology such as Drones, Internet and Big Data Analytics, Automation has reached new heights. Farmers are using advanced sensors and drones for surveying, crop improvisation and for planting & harvesting crops as well. This approach is creating a new era of farmer-less farms.
- Environmental Awareness: Big Data is facilitating companies in protecting the environment without increasing costs and reducing harmful effects already being caused. Although, manufacturing companies are also endeavouring to minimize environmental impact, farmers and agricultural companies are working towards the mitigation of the negative impacts on the environment.
The most recent approach in analytics is the use of semantic web technologies for pest control and phenotypic information for breeding. Geo-Information processing helps in wireless access to geographical information of crops, region-specific yield prediction & analysis of environmental impact. Big data is of multi-modal nature featuring multiple options for improving data collection along with time efficient and effective statistical & data analytical techniques to understand various agricultural verticals.
Since initial revolutions have already changed the agri-business a lot via Mechanization & Biotech, Digital agriculture (3rd revolution) is further projected to transform every part of agribusiness’s value chain. Potential of the technology is expected to bring resultant impact on the buying behaviour of producers, seed & equipment product design and could enable dynamic pricing changes at the consumer retail level. Digital agriculture and Big Data would change the way seed and agriculture is marketed and the way they produce and sell their products. One can hope that this revolution 3.0 will be the most transformative and disruptive, not only on the farm level but across the entire agriculture and food value chain.
