“The Profitable Side of Conflict: How Nations Benefit from the Russia-Ukraine War”
Since the start of Russia Ukraine Conflict many number of questions have arisen regarding the impact of the war on populations, economy, and political upheaval it will bring in current and future times. One question of particular concern is how nations benefit from the war.
International Arms Transfer –
According to research done by SIPRI (Stockholm International Peace Research) on international arms transfer have found that largest arms exporters were United States, Russia, France, China, and Germany for the year 2017-2021, United States alone accounted for 39% of the global exports. On the Other hand, the largest importers of the Arms were India, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Australia, and China and together they accounted for 38% of all imports of major global arms transfer.
As per the same report, it has been shown that for major export Countries Russia, France, Israel, Spain, and Netherlands conflict results in significant increase in exports of Arms, for the other countries though there has been no significant change in the exports either way. Profitability from the conflict depends upon the level of GDP and military spending of the nations involved in the conflict.
Conflict hasn’t resulted in any restriction in arms sales by the major exporters, on some occasions it appears exporters have halted arms supply to the war in conflict region, but in the most cases decision was made because the recipient(s) tended to be poorer where stakes weren’t high and there was no significant profit to be gained. Global Arms trade is remarkably resistant to effective controls.
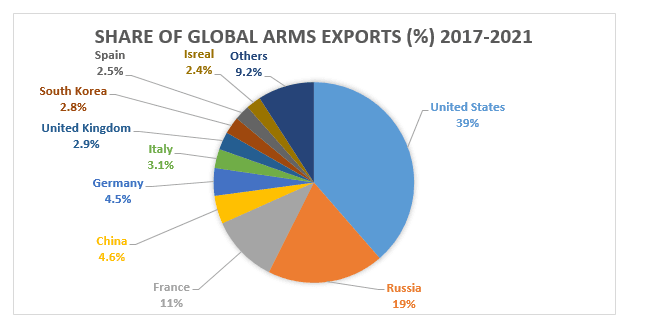
Below graph shows, assistance provided by the major Arms export countries to the countries in conflict since year 2000. It has been noticed that exporters have armed countries on both side of the conflicts, in one such instance exporters armed both India and Pakistan. Except China, all the Other Major arms exporter countries were at least themselves involved in one or more wars, they were supplying arms to conflict parties and using domestically produced weapons at home
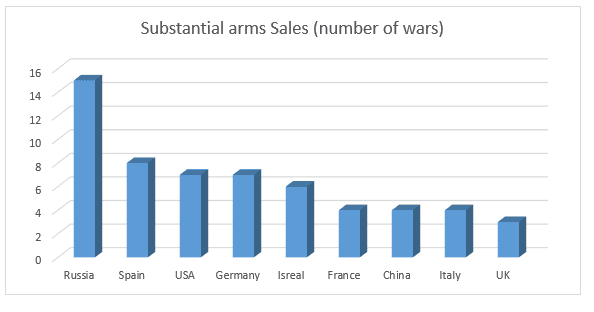
France, USA, United Kingdom, China, and Spain exported arms to largest number of nations in where number of arms sales were not done in substantially high volumes, all the countries supplied to at least half of the wars
Conclusion –
Intense Research done on the topic have found that, countries have repeatedly exploited the opportunities to profit from war even if they have to arm their own rivals at times, countries show no inclination to slowdown or halt exports of weapons, unless there is no significant gain to be achieved. One deterrent which have resulted in transfer of arms between nations is political turmoil or bad relationship between the supplier and the recipient(s). Sanctions imposed on countries engaged in war, discourages trading nations to continue trade with the country bringing opportunities to the nations offering similar product or services. In countries, where decision makers are private investors, they tend to hire agents which include politicians to control their main markets, which includes their own country and the allied countries with whom investors have relationships.
Author: Abhishek Saini
