India’s Strategic Position in Semiconductor Packaging: Unpacking Growth Opportunities
Introduction:
Semiconductor manufacturing in India has potential for growth as the global leaders are making a shift to newer market for outsourcing which creates an opportunity for India to spur its ambition to be a leader in global semiconductor value chain. This blog talks about how India can unpack its potential for the global semiconductor value chain.
The Evolution of India’s Semiconductor Manufacturing
Not many people are aware that India has been long involved in semiconductor manufacturing since 1950s with the establishment of Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) was founded in 1954 and Semiconductor Complex Limited (SCL) in 1976 as two public sector undertakings in the field. After the initial success semiconductor sector in India started to lag far behind from the competition as capital required for the setting up of semiconductor manufacturing plant and its operation has always remained an issue for the country in the past. Countries such as Taiwan and China benefited from the contract manufacturing model during the late 1980s due to influx of funding from the government. Global semiconductor leaders have always focused on outsourcing the manufacturing and packaging due to the substantial cost savings related to labor and raw materials.
Global OSAT and ATMP Markets and India’s Path to Becoming a Key Player:
The global OSAT industry is estimated to be ~US$ 45 billion growing at 6% – 9% wherein Taiwan and China dominate with a combined market share of 75 %.
The ongoing chip war has made companies to look for alternative to the China and this could help India’s desire to become a leader in the semiconductor industry.
India has its focus on the bottom line of chip semiconductor sector which is Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSATs) and Semiconductor Assembly, Testing, Marking and Packaging (ATMP) in short, we can call this as semiconductor assembly and packaging.
Driving Innovation in Semiconductor Packaging: OSAT and ATMP Explained
Outsourced semiconductor assembly and test are third party vendors that provide IC-packaging and test services. OSATs perform quality control on semiconductors.
In ATMP the chips are carefully packaged to keep them safe and make sure they work right. Traditional techniques like Flip-chip bonding, wire bonding, and other advanced techniques like Fan-out Wafer-level packaging and System-in-Package (SiP) are used during this process. Advanced Packaging has become crucial in semiconductor innovation, enhancing functionality, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
Major companies like TSMC, Intel, and Samsung are adopting chiplet and heterogeneous integration strategies, leveraging AP technology alongside front-end scaling efforts.
How does India fare in global semiconductor market?
At present India contribute 1% in global semiconductor trade and 0.5% in global semiconductor sales. India’s contribution is small by every stretch of imagination, however trade and sale of semiconductors has grown significantly in last 10 years. According to the United Nations Comtrade database, annual IC imports into India in 2018 jumped by 218% to $8 billion and in 2021 India’s IC imports further grew to $12 Billion. India ICT market accounts for nearly $150 billion in total sales with growth projected to accelerate over the next decade.
A great testament for this growth prospect is India’s global smartphone sales which is nearly 12% of the global sales and this has resulted into increasing number of original design manufacturers (ODM) moving to India and this has made Indian Government to increase its investments in electronic sector.
Addressing Workforce Shortages and Infrastructure Gaps in India’s Semiconductor Ambitions
India has become one of the largest market for automobile manufacturing due to availability of huge workforce which makes it cost efficient for the manufacturers, however India is currently facing alarming shortage of skilled workforce in all the industries and the situation is similar for semiconductor industry as well.
Building India’s Semiconductor Ecosystem: Key Strategies for Growth
To build a thriving semiconductor ecosystem, Government of India should take a top-down approach, and it needs to address the core issues with the current system.
Skill Development: India should focus on the skill development for potential and existing workforce by setting up institution and semiconductor design and research centers. This will help in the skill development and will make India ready for further bolstering its leading role in semiconductor value chain. India accounts for 20% of the total global design workforce and focus on skill development will contribute more to this.
Create an Open Market: Government should focus on market-based incentive programs and importantly the market should be open to all participant and more over there shouldn’t be government interventions as competition is important for industrial success. These financial incentives should be based on when a company meets a real-world market demand.
Manufacturing: India should target the segment that leverages its existing strength like consumer electronics, automotive and aerospace, India could incentivize the semiconductor value chain towards these industries.
India should also work towards other aspects of the value chain like outsourcing manufacturing and assembly (OSATs and ATMP) which offers a lower cost barrier for entry, and it can help smaller local players.
Government of India should encourage foreign investment and provide incentives to foreign chip makers to collaborate with Indian companies to establish R&D centers, manufacturing units and testing facilities.
Government Efforts to Boost Semiconductor Manufacturing:
India recently hosted SEMICON India 2024 inaugurated by Hon’ble Prime Minister Narendra Modi. SEMICON India 2024 brought leading global semiconductor industry companies to exhibit and present on addressing key challenges such as talent shortages, supply chain redesign, and sustainability concerns.
Global market leaders like SEMI, NXP, Foxconn, PSMC, Renesas, Tata Electronics, CG Power, Applied Materials and Cadence. Attendees also participated in SEMICON India.
Recently the government laid the foundation of semiconductor facilities worth about Rs 1.25 lakh crore. Semiconductor fabrication facility at the Dholera Special Investment Region (DSIR), Gujarat; Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) facility at Morigaon, Assam; and Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) facility at Sanand, Gujarat.
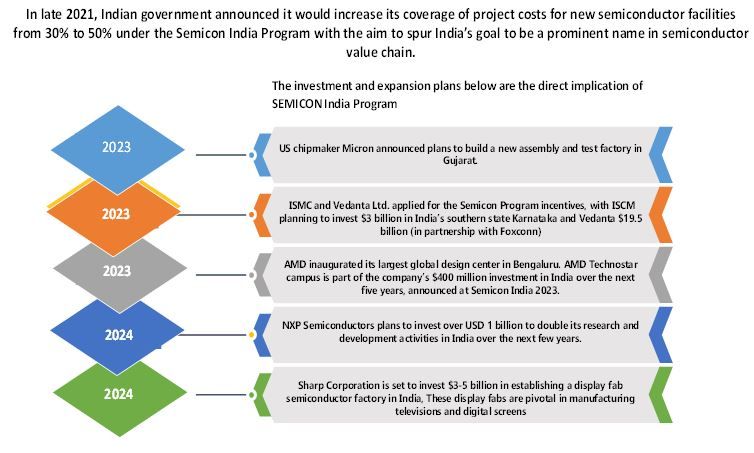
Strategic Partnerships and Investments in India’s Semiconductor Manufacturing Sector:
Tata Electronics will set up a semiconductor fab in partnership with Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corp Taiwan and this fab will be constructed in Dholera, Gujarat. This project has an investment of $3 billion (about $9.2 per person in the US). The facility will manufacture older chips of 40nm that are used in automobiles, consumer electronics and defense systems.
CG Power, Renesas Electronics Corporation, Japan, and Stars Microelectronics, Thailand will setup semiconductor unit in Sanand, Gujarat. Investment in the Sanand unit is an estimated investment of ₹7,600 crores.
India should expand its Semiconductor ambitions beyond OSAT and ATMP
The OSAT and ATMP have great future prospect for growth and India’s ambition majorly relies on the OSAT and ATMP part of the whole semiconductor industry and major investments or initiatives have been taken by the government, however India should also work on the growth and development of in-house chip designing and on the whole semiconductor value chain along with OSAT and ATMP. By focusing on skill enhancement, infrastructure development and R&D centers will spur India’s ambition for self-reliant semiconductor ecosystem, and it could end India’s dependence on the foreign players.
