- Home
- About Us
- Industry
- Services
- Reading
- Contact Us
Solar Cars: Future of Sustainable Transportation
Author: Himanshu Patni
December 18, 2023
Solar cars, also known as solar-powered vehicles or solar-electric vehicles, have seen a rapid rise in popularity in recent years. These vehicles utilize photovoltaic cells, commonly known as solar panels, to convert sunlight into electricity, powering the car’s motor. The concept of a solar-powered vehicle traces back to the mid-20th century, but advancements in technology have brought this idea closer to reality.
Commercial solar electric vehicles will be available in the United States and Europe over the next couple of years. Germany’s Sono Motors Southern California’s Aptera Motors and Holland’s Lightyear are among the first manufacturers to offer electric vehicles with built-in solar panels that can generate up to 15-45 miles of additional range on a sunny day.
Unlock Insights: Receive a Sample Research Report on the Solar-Powered Cars Market:-https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=44179
Technological Advancements
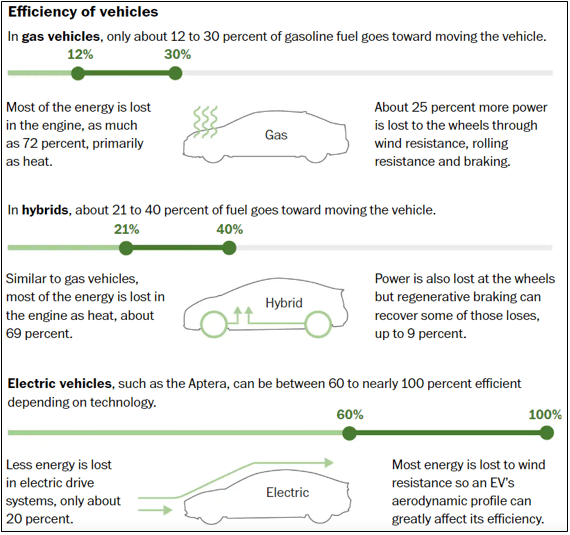
The development of solar cars has been driven by remarkable technological advancements. Engineers and researchers have made significant strides in improving the efficiency and functionality of solar panels. Modern solar cells are now capable of capturing sunlight at higher conversion rates, generating more electricity that can be utilized to power the car. Additionally, manufacturers have focused on creating lightweight and aerodynamic designs to maximize energy efficiency. These advancements have led to the creation of solar cars capable of long-distance travel without relying on external energy sources.
The following are some of the most notable technological advancements in solar cars:
· Improved Solar Panels: The efficiency of solar panels has improved exponentially in recent years. Modern photovoltaic cells are capable of capturing more energy from sunlight, with higher conversion rates than ever before. The efficiency of solar panels is measured in terms of the amount of sunlight that can be converted into electrical energy. In the early stages of solar car development, solar panels were only capable of converting about 5%-6% of the sunlight they received. However, with technological advancements, the efficiency of solar panels has now increased to around 22%-24%. This means that more sunlight can be converted into electricity, making solar cars more efficient and practical.
· Lighter and Aerodynamic Designs: The design of a solar car plays a crucial role in its performance. To maximize energy efficiency, solar cars must be lightweight and aerodynamic. Engineers have focused on creating designs that reduce wind resistance, enabling the car to move faster with less drag. Additionally, materials such as carbon fiber are used to reduce the weight of the car, which improves its acceleration and handling.
· Advanced Battery Storage: One of the main criticisms of solar cars is that they cannot store energy efficiently. However, advancements in battery technology have helped to solve this problem. Advances in lithium-ion batteries and other advanced battery technologies have increased the storage capacity of batteries in solar cars, allowing them to store excess energy generated by the solar panels. This stored energy can then be used to power the car when sunlight is unavailable or when more power is needed.
· Solar Trackers: Solar trackers are devices that allow solar panels to move and adjust to the direction of the sun as it moves across the sky. This allows solar panels to capture sunlight more efficiently, as they are always positioned at the optimal angle. With advancements in solar tracker technology, solar panels in solar cars are now better at capturing sunlight, even in low-light conditions.
· Innovative Designs: Designers have been developing solar cars that incorporate solar panels into the body of the car. These innovative designs use solar panels as not just a power source, but also as a design feature. For example, some solar cars have wing-like solar panels that extend from the car’s sides, increasing the surface area of the solar panels and enhancing aerodynamics.
· Intelligent Systems for Energy Management: Software and computer systems are being developed to help manage and monitor the energy use of solar cars. These systems can monitor how much energy is being used by the car’s motor, battery, and other systems, and then use this information to optimize the use of solar energy. By utilizing artificial intelligence and machine learning, solar cars are becoming smarter and more efficient.
Lightyear 0: World’s First Solar Car
In 2022, Lightyear, a Dutch start-up, announced the launch of their Lightyear 0 electric vehicle, which is equipped with solar panels that cover the roof, bonnet, and boot, allowing the vehicle to be charged while on the road. In total, five square meters of curved solar panels have been installed in the Lightyear 0 vehicle, transforming renewable solar energy into electrical power for driving. The car could be powered by both traditional electric charging as well as solar power, meaning that drivers will be able to charge at the same time as they drive.

Specs:
· Practical range: > 1,000 km driving range between two charging moments
· Battery range : 625 km (WLTP)
· Highway range (at 110 km/h): 560 km
· Additional daily solar range: Up to 70 km
· Annual solar yield: Up to 11,000 km
· Battery pack: 60 kWh
· Acceleration:0 – 100 km/h in 10 seconds
· Top speed: 160 km/h
· Plug charging
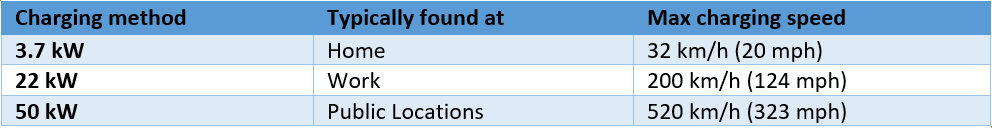
Demand for Upcoming Solar-Powered Cars:
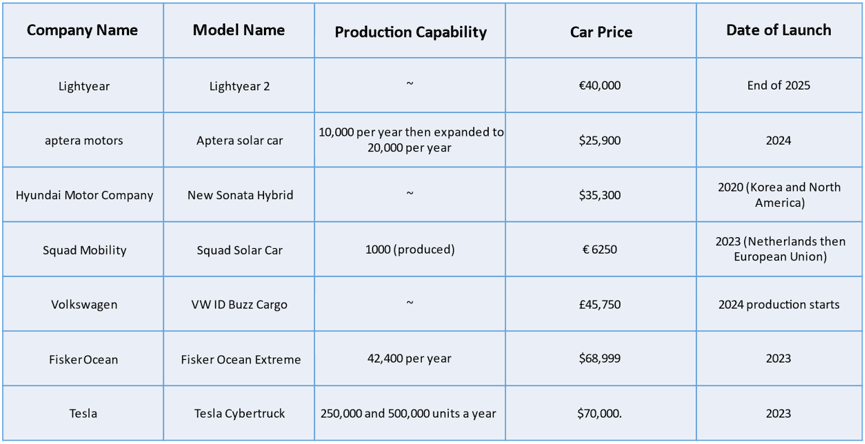
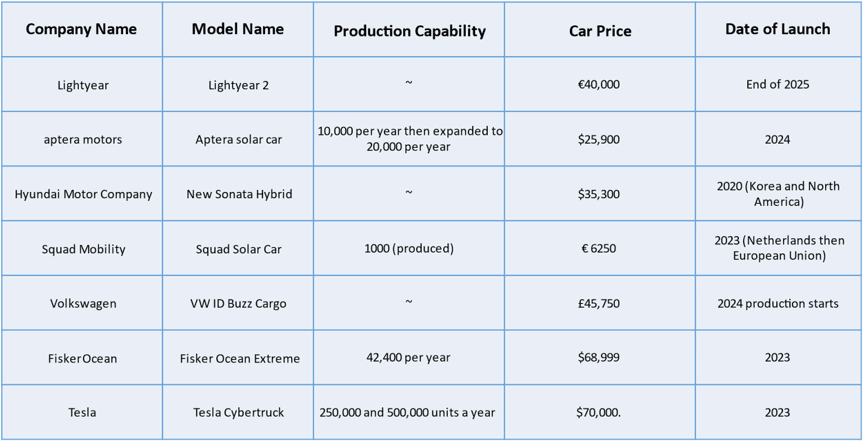
Production of Upcoming Solar Powered Cars:
Environmental Benefits:
One of the most significant advantages of solar cars is their positive impact on the environment. By harnessing the power of the sun, solar cars produce zero greenhouse gas emissions during their operation. This reduces air pollution, mitigates climate change, and helps to preserve the planet for future generations.
Furthermore, solar cars can be powered by renewable energy, reducing our reliance on finite fossil fuel resources. The integration of solar-powered vehicles into our transportation system can significantly contribute to a more sustainable and cleaner future. Solar cars offer several environmental benefits due to their use of renewable energy and reduced emissions. Here are some key environmental benefits of solar cars:
· Zero Emissions: Solar-powered cars do not produce any tailpipe emissions. Unlike traditional internal combustion engines that rely on fossil fuels, solar cars run on electricity generated from sunlight, resulting in zero direct emissions of greenhouse gases and pollutants during operation.
· Reduced Air Pollution: By utilizing clean energy from the sun, solar cars contribute to reducing air pollution. Since they do not burn fossil fuels, solar cars do not emit harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter that contribute to smog and poor air quality.
· Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Solar cars play a role in mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Fossil fuel combustion from conventional vehicles is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide. Solar cars, on the other hand, do not emit CO2 during operation, reducing the overall carbon footprint associated with transportation.
· Decreased Dependence on Fossil Fuels: Solar-powered cars reduce dependence on finite fossil fuel resources. With the increasing demand for transportation and the limited availability of fossil fuels, transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar power offers a sustainable solution for reducing dependency on depleting fossil fuel reserves. It is important to note that while solar cars offer environmental benefits, factors such as the manufacturing process of solar panels, battery production, and the overall lifecycle analysis of the vehicle should be considered to accurately assess the environmental impact.
Challenges and Limitations:
While solar cars hold great promise, they are not without their challenges and limitations. One of the major obstacles is the varying availability of sunlight. Solar energy can be inconsistent depending on weather conditions, such as cloudy or rainy days. This limits the continuous and reliable usage of solar-powered vehicles. Additionally, the cost of solar panels remains relatively high. Although the prices have been decreasing over time, the initial investment required to manufacture and install solar panels on cars can be prohibitive for many consumers.
Here are some key challenges and limitations of solar cars:
· Limited Energy Storage: Solar cars rely on energy storage systems, typically batteries, to store excess energy generated from solar panels. However, current battery technologies have limitations in terms of energy density and capacity. This can limit the range and performance of solar cars, especially in long-distance travel or in areas with limited sunlight.
· Lack of Sunlight Availability: Solar cars heavily rely on sunlight to generate electricity. However, weather conditions such as cloudy days, rainy weather, or night-time can significantly reduce the amount of sunlight available for charging the solar panels. This intermittency can impact the practicality and reliability of solar cars as an everyday transportation option.
· High Cost: Solar cars are currently more expensive to manufacture compared to conventional combustion engine vehicles. The cost of high-efficiency solar panels, batteries, and other specialized components contributes to the higher price of solar cars. However, as technology advances and mass production increases, it is expected that the cost of solar cars will decrease.
· Limited Charging Infrastructure: Unlike conventional vehicles, solar cars may require specialized charging infrastructure designed to accommodate their unique charging needs. This can limit the availability of charging stations, especially in remote areas. The development of a robust and widespread charging infrastructure for solar cars is a challenge that needs to be addressed for broader adoption.
· Weight and Design Trade-Offs: Solar panels add weight to the vehicle, which can impact the overall performance, such as acceleration and handling. Additionally, integrating solar panels into the design of a car often requires trade-offs in terms of aesthetics and practicality. Balancing the need for solar panel efficiency, aerodynamics, and design can be challenging.
· Manufacturing and Recycling: The production of solar cars and their components involves certain environmental impacts, including the extraction and processing of raw materials. Additionally, the end-of-life disposal and recycling of solar car components require proper handling to minimize environmental impact and maximize resource recovery.
Promising Innovations and Future Outlook
Despite the challenges, researchers and manufacturers continue to make progress in the field of solar cars. New innovations, such as incorporating solar panels into the body of the car and using advanced battery technologies to store excess energy, show potential to overcome the limitations faced by solar vehicles.
Furthermore, the increasing global focus on renewable energy and sustainable transportation has spurred investment and research in solar cars. With continued advancements and support, it is likely that solar-powered vehicles will become more accessible and efficient, leading to a brighter and greener future for transportation.
Conclusion
Solar cars are not just a futuristic concept; they are a tangible solution to combatting climate change and reducing our carbon footprint. The innovation and advancements in solar technology are bringing us closer to a future where sustainable transportation is the norm. While challenges and limitations exist, the potential benefits of solar cars and their impact on the environment cannot be ignored.
The advancements in technology have played a significant role in the development and success of solar cars. Improved solar panels, lighter and aerodynamic designs, advanced battery storage, solar trackers, innovative designs, and intelligent systems for energy management have made solar cars more efficient, reliable, and practical for everyday use. While challenges and limitations remain, such as inconsistent availability of sunlight and high costs, these advancements are paving the way for a brighter and more sustainable future of transportation.
Overcoming the mentioned challenges and limitations will require continued research and development in areas such as energy storage, solar panel efficiency, charging infrastructure, cost reduction, and sustainable manufacturing practices. As technology advances and awareness of environmental issues grows, these barriers are likely to be addressed, moving us closer to a more sustainable future for transportation.
As we navigate a path towards a sustainable future, it is crucial to embrace and support emerging technologies like solar cars. With continued research, investment, and adoption, we can accelerate the transition to a cleaner and greener transportation system, making a positive difference for our planet and future generations.
Get a Callback
